Remote Pair Programming via SSH and wemux on Linux
There are several benefits to the use of pair programming in the software development process: fewer mistakes, better understanding of the codebase across multiple developers, and improved team cohesiveness (cf. The Pros and Cons of Pair Programming). Personally, I have found pair programming can be especially useful for training. Experienced developers forget the multitude of tiny stumbling blocks that less experienced developers encounter on a daily basis. Also, it can be helpful for less experienced developers to see how experienced developers have customized their tools for increased productivity (e.g., terminal setup, emacs config, vim config, etc.)
However, when working remotely, pair programming can be difficult without a simple and secure process. In this post, I describe the steps required to setup a secure pair programming process in which one (remote) developer SSH’s into another (host) developer’s Linux machine. The host developer will be able to specify which remote developers have access and also see the command line keyboard entries made by the remote developer. We will also configure the host machine such that the remote user will not be able to SSH into the host machine unless the host developer runs a specific terminal sharing program (i.e., wemux). While this setup is fairly secure, you shouldn’t grant access to remote developers that you don’t trust.
System Overview
A high-level diagram of the setup is shown in the following figure.
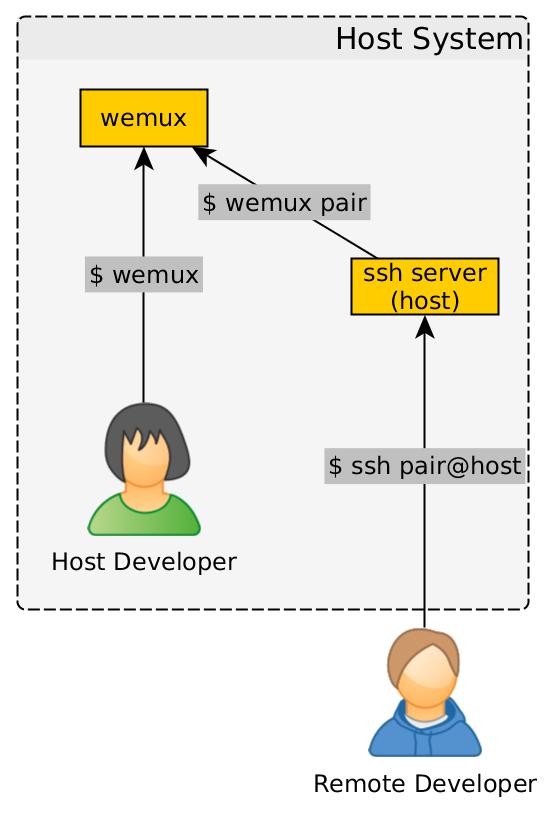
As shown in the diagram, the pair programming server is initiated by the host
developer running the wemux command. The remote developer then uses SSH to
log into the pair Linux user on the host machine. The pair user’s
~/.profile file is configured to run the command, wemux pair; exit, which
forces the remote user to immediately join the wemux session upon login and
exit the SSH session when the wemux session ends. Finally, to make it easier to
SSH into computers that are behind firewalls, proxies, and VPN servers, the
host machine will use ngrok to provide an SSH tunnel (cf. ngrok).
One-Time Host Linux Machine Configuration
Install Package Dependencies
Install the SSH server, tmux, and the snap package manager with your system’s package manager:
$ sudo apt-get install openssh-server tmux snapdInstall the ngrok snap package
ngrok will be used to create an SSH tunnel to the host machine that can be securely accessed behind firewalls and VPN servers.
$ sudo snap install ngrokConfigure ngrok
Create an ngrok account: https://dashboard.ngrok.com/login
After creating your ngrok account, you will need to use the tunnel
authorization token in your ngrok account to authorize your machine. Copy the
authorization token from the website,
https://dashboard.ngrok.com/auth, and run
the following command, where <authorization-token> is the copied token:
$ ngrok authtoken <authorization-token>Install and Configure wemux
wemux is a project that allows multiple developers to directly collaborate on the same command line. (wemux leverages tmux.) First, clone the wemux project to a local directory. Typically, I keep 3rd-party repositories in a separate directory:
$ mkdir -p ~/repos/3rd-party
$ cd ~/repos/3rd-party
$ git clone https://github.com/zolrath/wemux.gitNow, configure wemux to only allow the host user to start a wemux session:
$ cd wemux
$ echo "host_list=(${USER})" >> ./wemux.conf.exampleSymbolically link the wemux executable to a directory that is on the system
$PATH and link the configuration file to the default location (you will need
to run the following commands with sudo):
$ sudo ln -s $(pwd)/wemux /usr/local/bin/wemux && \
sudo ln -s $(pwd)/wemux.conf.example /usr/local/etc/wemux.confCreate a new Linux User
We will create a new Linux user, called pair, that will only be used by
remote pair programming users. You can accept the default values when running
the adduser command, but make sure you specify a non-trivial password for the
new user.
$ sudo adduser pairNow that the user has been created, let’s modify the user’s ~/.profile file
such that when the remote user logs in, they are immediately dropped into the
currently running wemux session.
$ sudo /bin/bash -c "printf \"wemux pair\nexit\n\" >> /home/pair/.profile"If the remote user tries to log into the pair user and the host isn’t running
wemux, then the user’s SSH session is immediately terminated. Through this
mechanism, the host developer specifies when the remote user can access the
pair user. Also, the exit command terminates the pair user’s session
when the wemux session ends.
To hold the public keys from remote developers, let’s create the
authorized_keys file for the pair user:
$ sudo /bin/bash -c "mkdir -p /home/pair/.ssh && touch /home/pair/.ssh/authorized_keys"For additional security, let’s configure the SSH server such that the pair
user can’t login with a password and then we’ll restart the SSH server:
$ sudo /bin/bash -c "printf \"Match User pair\n PasswordAuthentication no\n\" >> /etc/ssh/sshd_config"
$ sudo service ssh restartHost Machine Session Initiation
The following are the typical steps required when initiating a new pair programming session.
Enable SSH Login via Public/Private Key Authentication
The remote user will log into the pair user, but we don’t want the remote
user to have to know the password for the pair user, so we will use
public/private key authentication for SSH login. The remote user needs to send
their public key (typically located at ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub) to the host
developer. If the remote developer hasn’t generated SSH keys yet, the remote
user should generate SSH keys with the following command (substituting a valid
e-mail address):
$ ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "your_email@example.com"The id_rsa.pub file can be transferred to the host developer via e-mail,
chat, etc. Upon reception of id_rsa.pub, the host developer can add the
public key to the pair user’s authorized_keys file to enable password-less
SSH login:
$ sudo /bin/bash -c "cat id_rsa.pub >> /home/pair/.ssh/authorized_keys"Expose SSH Port via ngrok
The host developer will now use the ngrok command to expose port 22 of the
SSH server:
$ ngrok tcp 22The ngrok connection information will be printed to the screen. Note the information in the “Forwarding” section as this will be sent to the remote developer to access the host’s SSH server. For example, if the “Forwarding” section contained the following information:
Forwarding tcp://0.tcp.ngrok.io:14242 -> localhost:22The remote user would use the following SSH command to log into the host’s
machine (the -p flag specifies the SSH port):
$ ssh -p 14242 pair@0.tcp.ngrok.ioStart wemux Host Session
The remote developer will not be able to log into the pair user until the
host developer starts the wemux session in a separate terminal:
$ wemuxAt this point, the remote developer can run the previously shown SSH command. When, the host exits the wemux session, both users will be removed from the session and the remote user will be logged off.
Configuration Options
wemux options
If you don’t want the remote user to be able to enter commands, you can force
the remote user into the “mirror” mode by changing wemux pair to wemux
mirror in the ~/.profile file.
Other Notes
After you modify the pair user’s ~/.profile file, you won’t be able to
easily log into pair user with the normal su pair command without having to
start the wemux server. Instead, you can just directly modify the user’s
configuration files by prefixing your editor call with sudo:
$ sudo nano /home/pair/.profileReferences
The following blog posts were used to put together this post:





Leave a comment